Application
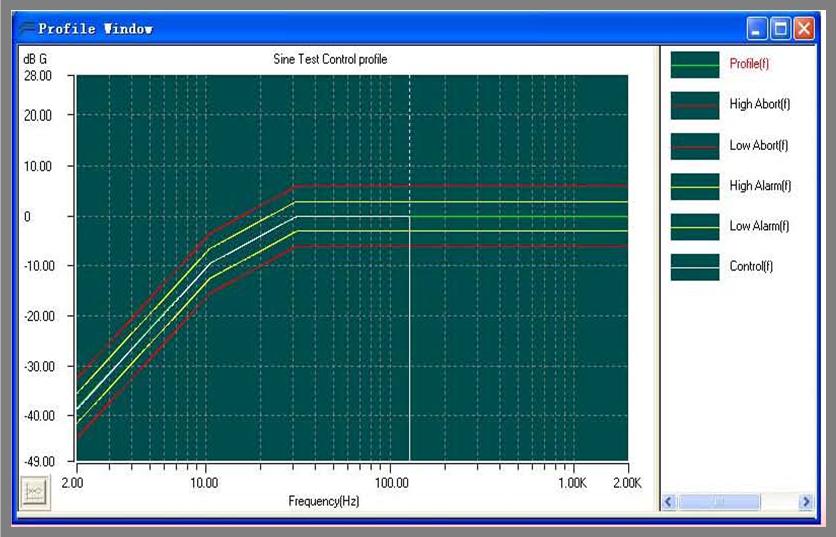
Sine Vibration Testing
In sine vibration testing, the sinusoidal force with fixed or sweeping frequency is induced into the component under testing with controlled amplitude (displacement/ velocity/ acceleration). It is useful in determining the natural frequency/ resonance of the component as only one frequency is present at a particular instance and also to carry out the study of structural response for fatigue simulation. The product is tested for all the frequencies in the given bandwidth to ensure it’s robustness and durability.
|
|
|
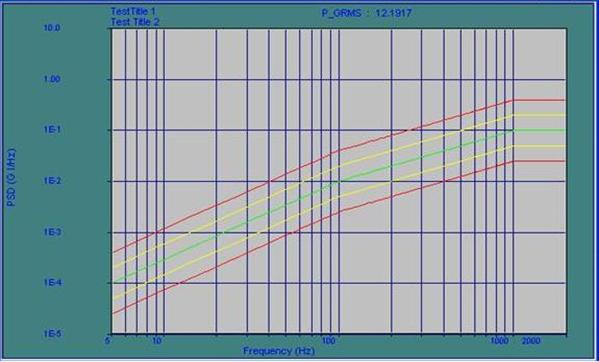
Random Vibration Testing
In random vibration testing, the random force containing a band of frequencies is induced into the component under testing with average targeted frequency content and amplitude over the duration of the test. Random vibration represents real world data which is encountered by the component during usage. As it excites all resonant frequencies simultaneously, it is well suited for production stress screening, prototype testing and vibration qualification of products to various standards.
|
|
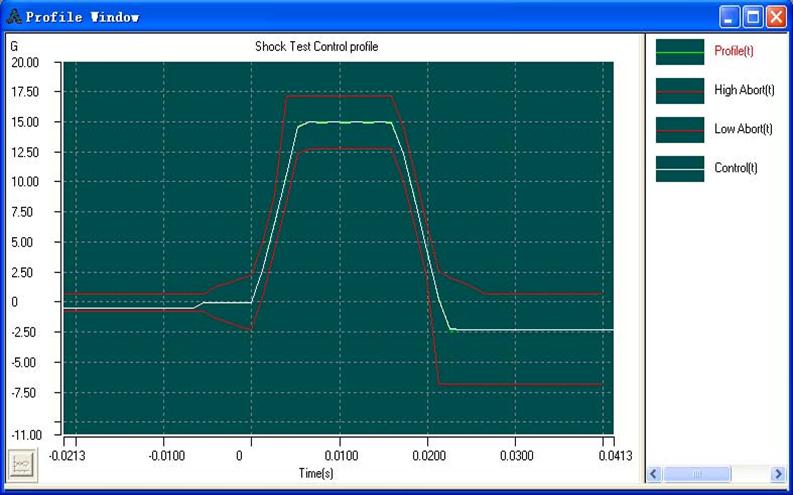
Shock Vibration Testing
Shock and bump testing is though also conducted using various dedicated shock machines for product qualification, but advent of advanced control algorithms and pulse synthesis techniques have resulted better control accuracy and repeatability in drop simulations on electrodynamic shakers. These shock and short duration transient vibrations are produced and controlled with real time adaptive control process. However, electrodynamic shakers do pose certain restrictions because of limited stroke length and power output capability of amplifier which drive the shaker. It’s quite easy for the user to select any kind of waveform (half sine, saw tooth, square, rectangular, trapezoidal, user defined shapes etc.) through software and perform the test without any hassle.
|
|
|
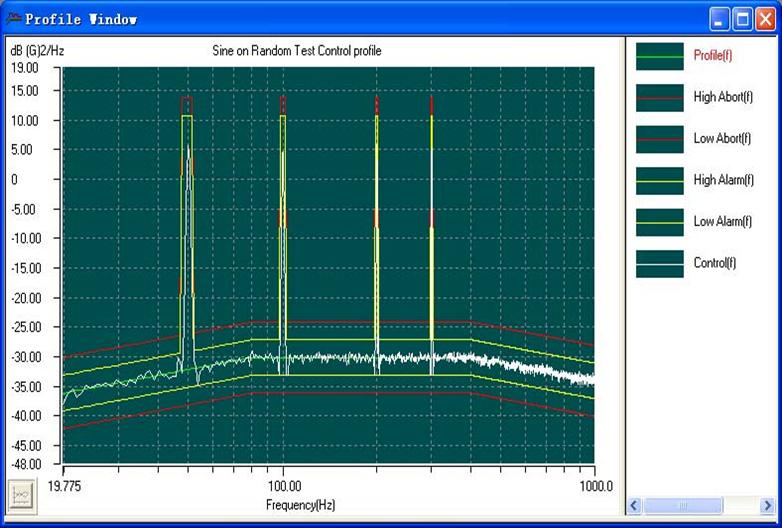
Mixed Mode Testing (SOR,ROR,SROR)
Mixed mode testing is applicable in the case where the component is likely to be exposed to vibration environment consisting of wideband energy in addition to sinusoidal and narrowband energies superimposed on it for continuous or short durations. The vehicle engine in automobiles and rotor blade in helicopters are well known examples generating continuous sine vibration onboard with broadband random vibration being induced by turbulence.
|
|
Combined Testing
Demand of combined testing (vibration + temperature together) is growing in all sectors as this method not only reduces the evaluation period but also creates more realistic environmental conditions in which the component has to function. The vibration shaker can be attached/ detached with the environmental chamber for vertical and horizontal integrated operation with vibration cycling and temperature cycling (hot/cold/humidity) running simultaneously in interlocked mode.
|
|
|
Fatigue Testing
Fatigue testing is generally done on mechanical components simulating the resonating conditions for longer period. Initially, resonant frequencies of the component are identified by sweeping sine method and then resonance dwelling and tracking test is performed which is also called Tracked Dwell. Tracked dwells are applied for fatigue testing of high-cycle critical components such as crank shafts, turbine blades, aircraft blades etc.
|
|
|
|
About Us
We are a trusted source for environmental testing solutions in present economical scenario.
Contact
- Khasra No. 986M & 987, Salampur, Rajputan Indistial Area, Roorkee, Uttarakhand - 247667
- +91-9012345127, +91-9837391375
- +91-1332-268848
- info@pacific-dynamics.com
- -- Website Here --






